Is A Global Recession Imminent?

Since the beginning of 2022, the world witnessed a rapid deterioration of growth prospects coupled with rising inflation and tightening financing conditions. Altogether, the conditions have ignited a debate about the possibility of a global recession with contractions in global per capita GDP. World Bank has forecasted a global recession that has already materialized in recent times or is underway. The forecast has suggested that every global recession since 1970 was preceded by a significant global growth weakening in previous years. Also, all previous global recessions coincided with sharp slowdowns in several major economies. This heightens the likelihood of a global recession in near future.
Also Read: The pandemic depression: A global recession that will take years to recover
Near- Term Growth Outcomes
7 out of 10 economists at the World Economic Forum held in Geneva in September 2022 believe reduced growth, stubbornly high inflation, and real wages to continue till 2023, bringing in a global recession. Given below is the table showing economic growth and employment growth o different regions of the world.
| Region | Economic Growth | Employment Growth |
| United States | 37% | 45% |
| Latin America & the Caribbean | 24% | 56% |
| Europe | 14% | 35% |
| Middle East & North Africa | 71% | 80% |
| Central Asia | 44% | 60% |
| South Asia | 77% | 80% |
| China | 66% | 69% |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 47% | 40% |
| East Asia & Pacific | 61% | 81% |
The cost of living crisis is driving concerns around energy and food prices. Sub-Saharan Africa and MENA region expect food insecurity. Saadia Zahidi, Managing Director at the World Economic Forum stated that growing inequalities between and within countries due to the ongoing legacy of COVID, war, and uncoordinated policy action, inflation soaring, real wages falling, has caused global cost of living crisis, hitting the vulnerable the most. “As policymakers aim to control inflation while minimizing the impact on growth, they will need to ensure specific support to those who need the most”, he further added.
World Bank has suggested three scenarios for the global economy that have been analyzed for 2022-24 using a large-scale, cross-country model.
 If the ongoing global slowdown turns into recession, the global economy could end up experiencing large permanent output losses relative to its pre-pandemic trends. Thus having severe consequences for long-term growth prospects of emerging markets and developing economies that were already hit hard by the pandemic-induced global recession of 2022.
If the ongoing global slowdown turns into recession, the global economy could end up experiencing large permanent output losses relative to its pre-pandemic trends. Thus having severe consequences for long-term growth prospects of emerging markets and developing economies that were already hit hard by the pandemic-induced global recession of 2022.
Pandemic’s Swift Yet Massive Shock
The shutdown measures of coronavirus pandemic to contain it have plunged the global economy into a severe contraction. In 2020, World Bank announced 5.2% shrink in the global economy, the deepest recession since the Second world war. Its Global Economic Prospects stated that the largest fraction of economies are experiencing a decline in per capita output in June 2020, since 1870. As domestic demand and supply, trade and finance severely disrupted, economic activities among advanced economies shrunk 7% in 2020.
Ceyla Pazarbasioglu, World Bank Group Vice President for Equitable Growth, Finance and Institutions called it a deeply sobering outlook as crisis were expected to leave long-lasting scars. Highlighting the major global challenges he said, “our first order of business is to address the global health and economic emergency. Beyond that, the global community must unite to find ways to rebuild as robust a recovery as possible to prevent more people from falling into poverty and unemployment”.
The same year, the World bank projected that emerging markets and developing economies shall shrink by 2.5% with 3.5% decline in per capita incomes, the first contraction as a group in at least sixty years. The blow hit hard in countries where the pandemic has been most severe, tipping millions of people into extreme poverty. The magnitude of disruption varied over regions, but all EMDEs had vulnerabilities that were magnified with external shocks.
Experts believe that covid pandemic badly affected Sri Lanka’s tourist trade- one of the biggest foreign currency earners for the nation. In 2019, Sri Lanka faced deadly bomb attacks that frightened off the tourist. At the end of 2019, Sri Lanka had $7.6 billion in foreign currency reserves which dropped to $250 million in 2022. Additionally, the big tax cuts introduced in 2019 to boost goods in the domestic market lost government’s $1.4 billion annual income. People have been struggling with daily power cuts and shortages of basic necessities like fuel, food, and medicine as inflation (in CPI) running more than 50%.
Indonesia is one such country wherein its economy is based on the tourist trade and was worst hit with the Delta variant. The Indonesian economy continued to recover in 2021 and expanded at 3.7% in 2021 and 5.2% in 2022 (WB, 2021). The country nailed the global financial conditions and avoided the scarring effects of the crisis by introducing pandemic-responsive fiscal sustainability. It adopted Tax Harmonization Law to address the low tax collection rates. Moreover, the structural reforms were crucial to bringing in a more competitive, resilient, and greener economy.
Financial Systems
After more than a decade after the Lehman Brothers collapse, one question about the financial system keeps coming up; Are we safer than we were in 2008? To be short- yes, but not safe enough! It is true that bans over the world now have bigger and better capital buffers and more liquidity, but more needs to be done. Regulation and supervision have been strengthened as countries have taken steps to address systematic risks posed by institutions seen as too big to fail.
International agencies like IMF have improved their ability to analyze and monitor systematic risks. Further, it partnered with national authorities to help them identify potential trouble spots. Despite this, central banks all over the world have hiked interest rates as a response to inflation creating a string of financial crises in EMDEs, thus, edging towards global recession in 2023.
According to a new study by World Bank, central banks have been raising interest rates this year with a degree of synchronicity not seen in the past 50 years. The trend is likely to continue next year too, and if so, the policy actions may be insufficient to bring back global inflation back down to levels seen before the pandemic.
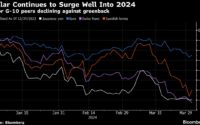
Global consumer confidence has suffered a much sharper decline as the world’s three largest economies- the United States, China, and Euro area have been slowing sharply.
 Looking at the situation since 1970s-1982 in the above diagram, central banks should persist in their efforts to control inflation. Meanwhile, central banks should also communicate policy decisions clearly while safeguarding their independence. This can further help anchor inflation expectations and reduce the degree of tightening needed. While in advanced economies, central banks should keep in mind cross-border spillover effecting the monetary tightening, in EMDEs, they should strengthen macroprudential regulations and build foreign-exchange reserves.
Looking at the situation since 1970s-1982 in the above diagram, central banks should persist in their efforts to control inflation. Meanwhile, central banks should also communicate policy decisions clearly while safeguarding their independence. This can further help anchor inflation expectations and reduce the degree of tightening needed. While in advanced economies, central banks should keep in mind cross-border spillover effecting the monetary tightening, in EMDEs, they should strengthen macroprudential regulations and build foreign-exchange reserves.
Policy Responses
To sustain the economic momentum and prevent the effects of the pandemic from leaving lasting economic and social scars, the economies will have to focus on policy responses to strengthen investment, accelerate human capital accumulation, and boost productivity. Further, some measures to ease the constraints that confront labor markets, energy markets, and trade networks shall help support the growth.
At micro-level, policymakers must navigate a narrow path with a comprehensive set of demand and supply side measures. On the demand side, monetary policy must ensure price stability and fiscal policy must prioritize medium-term debt sustainability while providing targeted support to vulnerable groups.
Fiscal authorities must carefully caliberate the withdrawal of fiscal support measures whule ensuring consistency in the objectives of monetary policy. The fraction of countries planning to tightening their fiscal policies are expected to reach highest levels since early 1990s. Here are some strong steps that are suggested to fight inflation;
- Easing the labor-market constraints by increasing labor-force participation and reducing price pressure.
- Boosting the global supply of commodities with increase in food and energy supply.
- Lastly, strengthening global trade networks wherein policymakers cooperate to alleviate global supply bottlenecks.
Summary
Article Name
Is A Global Recession Imminent?
Description
The forecast has suggested that every global recession since 1970 was preceded by a significant global growth weakening in previous years. Also, all previous global recessions coincided with sharp slowdowns in several major economies. This heightens the likelihood of a global recession in near future.
Author
TPT News Bureau
Publisher Name
THE POLICY TIMES
Publisher Logo

[ad_2]
Source link